Logical Architecture
The SRE is composed of several instances grouped into 2 distinct instance types:
- the Element Manager (EM): 2 instances
- the Call Processing (CP): N instances (depending on the implementation)
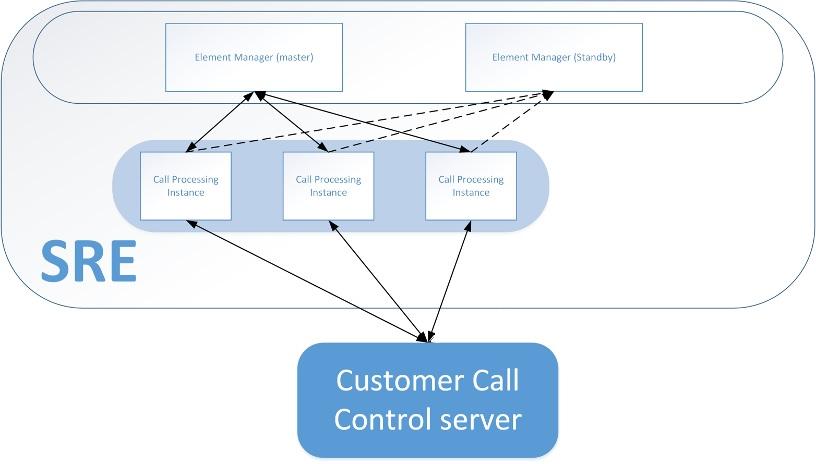
These instance types are interconnected.
The CP instances are interconnected with the Customer existing Call Control Server (SBC).
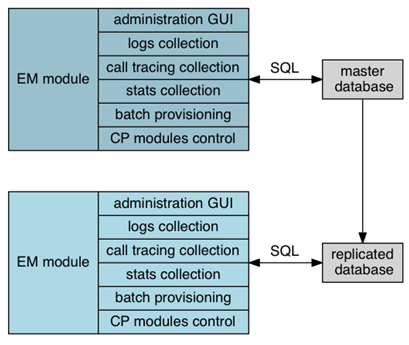
Element Manager Instances
The EM instances are responsible for handling the following functions:
- hosting the local database (master-slave model with replication)
- administration GUI
- logs centralization
- call tracing centralization
- stats centralization
- batch provisioning
- control of the CP modules
- CDR production and control
For redundancy purpose, two element managers are deployed, one as Master and the other one as Slave (hot standby).
One of the EM instances acts as master for the PostgreSQL database. The database is replicated to the second instance thanks to the streaming replication feature of PostgreSQL (RPM). This second node, which acts as a hot standby under normal operations, is ready to take over the master role. At that point, CP instances must in turn be updated to use this new master for their own replicated databases.
Call Processing Instances: Layered Architecture
Depending on the amount of traffic and for redundancy purposes, multiple CP instances can be deployed.
Several CP instances are responsible for handling the following functions:
- acting as replicated database
- processing INVITE/ENUM/HTTP requests from any network platform
- processing OPTIONS polling to provide a correct health state indication and node isolation if needed collecting and sending logs, call tracing information and stats to the EM instances.
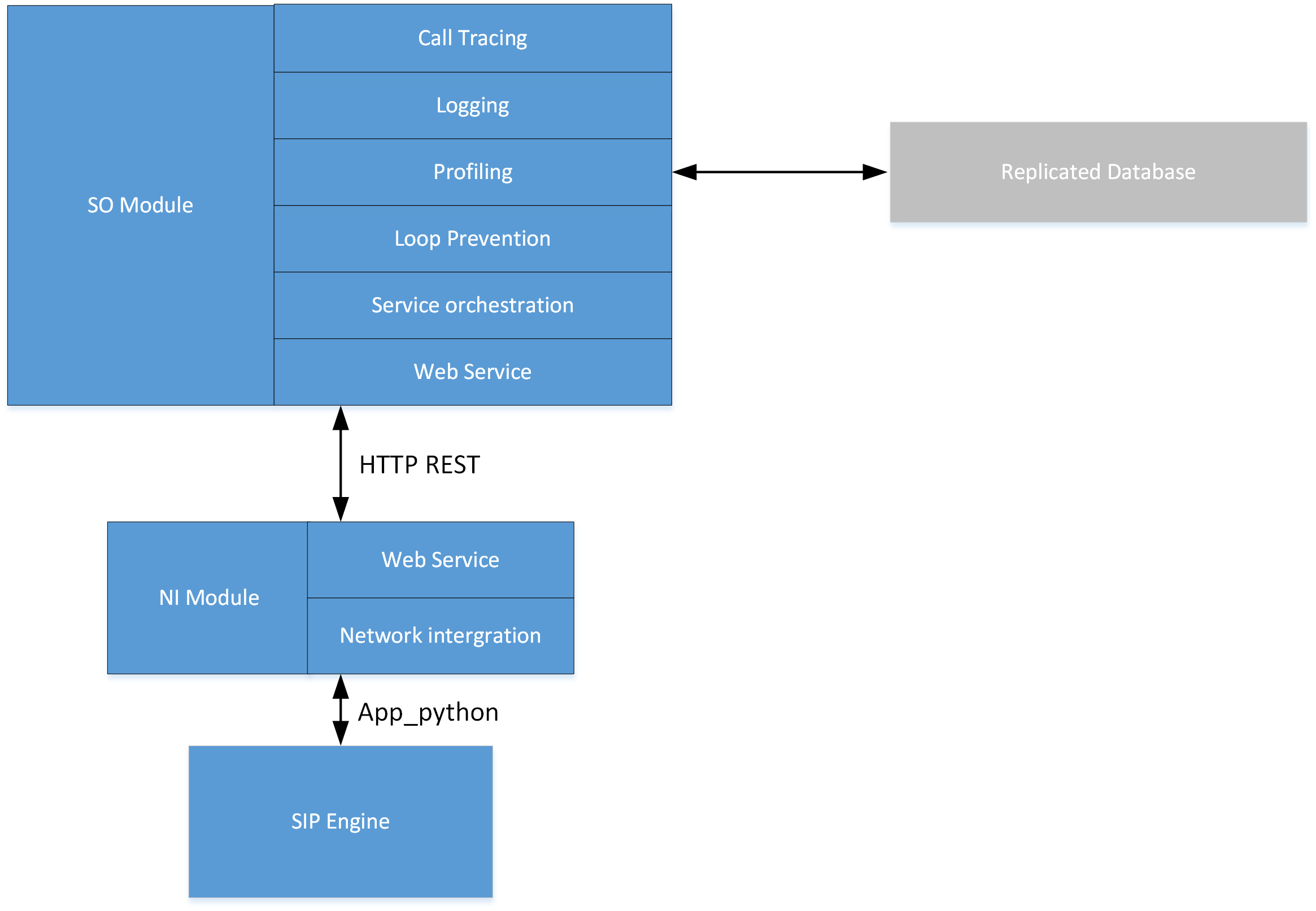
The layered architecture provides a modular, extensible, and future-proof model.
The first layer is the SIP engine element acting as the SIP interface towards the voice network and the business logic.
This business logic is composed of 2 modules:
- the Service Orchestration (SO) module.
- the Network Interaction (NI) module.
The CP instances are designed in a way to continue handling calls in case of connectivity loss with the EM layer. As such, they are self-contained call processing instances, able to work in an isolated mode until connectivity is restored.
Infrastructure/Hardware Requirements
Operating System Requirements
SRE can be installed on the latest RedHat 8.x release.
CPU and Memory Requirements
The minimum requirements for an SRE server are:
- vCPU: 4
- Memory Size: 8192 MB
- Hard Disk Size: 200GB (SSD)
INFO
A more tailored dimensioning is needed on a project basis.
Networking Requirements
SRE should be equipped with a minimum of 1 Gigabit Ethernet link.
Element Managers can be configured with 1 or 2 NIC interfaces
- 1 for Management (GUI/SSH access)
- 1 for DB replication between all components (EM's and CP's) and for CP modules control
INFO
They can be combined in a single interface
Call Processors can be configured with multiple NIC Interfaces
- 1 for Management (SSH access)
- 1 for DB Replication and access to the element Managers
- 1 or more for the Call Processing in case SRE needs to communicate with multiple voice networks.
INFO
They can be combined in a single interface
Communication Matrix
| Source | Destination | Interface | Protocol/DestinationPort | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| terminal | EM | management | TCP/22 | ssh/sftp |
| EM | CP | internal | TCP/22 | ssh |
| browser | EM | management | TCP/8080 (*) | http/https GUI access |
| external provisioners | EM | management | TCP/5000 (*) (**) | REST APIs |
| EM | DNS server | management | UDP/53 (**) | dns resolution |
| EM/CP | NTP server | management | UDP/123 | time synchronization |
| EM | EM | internal | TCP/5432 | DB traffic |
| CP | EM | internal | TCP/5432 | DB traffic |
| CP | CP | internal | TCP/5555 (*) (**) | kamailio-broker traffic for hitless update |
| CP | EM | internal | TCP/5000 (*) | db updates from service logic |
| CP | EM | internal | TCP/10000 | SRE log and stats |
| CP | EM | internal | TCP/10001 | SRE internal requests |
| CP | EM | internal | TCP/10002 | Accounting data |
| EM | EM | internal | TCP/10003 | Accounting synchronization |
| EM | SNMP managers | management | UDP/162 (*) (**) | SNMP traps |
| EM | SMTP server | management | TCP/587 (**) | mail server |
| EM | syslog server | management | UDP/514 (*) (**) | syslog data |
| EM | LDAP server | management | TCP/389/636 (*) (**) | GUI authentication |
| SIP endpoint(s) | CP | SIP | UDP/TCP/5060 (*) (**) | SIP traffic interface |
| HTTP endpoints | CP | HTTP | TCP/6000 (*) (**) | http traffic interface |
| ENUM endpoints | CP | ENUM | UDP/TCP/53 (*) (**) | ENUM traffic interface |
(*) port can be customized (**) optional
Software Requirements
SRE 4.0 requires the following software:
- postgres 14
- influxdb 2.4 (only on EMs)
- kamailio 5.7 (only on CPs)
- mongodb 5.0 (only if CAC or global caching is configured)
Operating System Configuration
Disk partitioning
Create the necessary partitions according to the table below.
The example below is sized for a total disk space of 250GB.
| Partition | Size | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| /boot | 1GB | Ext4 or XFS on LVM | boot partition |
| /boot/efi | 200 MB | EFI s.p. | The EFI System Partition is required for UEFI-based platforms that no longer use the legacy Master Boot Record (MBR) partition table. |
| /opt | 5 GB | Ext4 or XFS on LVM | SRE software |
| /var/log | 10 GB | Ext4 or XFS on LVM | system and SRE logs |
| /var/lib/pgsql | 65 GB | Ext4 or XFS on LVM | PostgreSQL database |
| /data/sre/db/backups | 50 GB | Ext4 or XFS on LVM | workspace for backups |
| /data/sre/db/wals | 20 GB | Ext4 or XFS on LVM | work-ahead logs |
| swap | 8GB | Swap | |
| /data/sre/provisioning | 10 GB | Ext4 or XFS on LVM | provisioning data (EM only) |
| / | 30 GB | Ext4 or XFS on LVM | |
| /var/lib/mongo | 10GB | Ext4 or XFS on LVM | Mongo database (only if CAC or global caching is configured) |
INFO
Unused space is reserved for future expansion.
Networking
Normally, you should have configured the different network interfaces during the OS installation. If not (or if you want to modify or check the configuration) update the file ifcfg-eth0 in /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ with the IP interface information:
| Parameter | Value | Example |
|---|---|---|
| BOOTPROTO | static | static |
| IPADDR | eth0 Interface IP address | 10.0.11.30 |
| NETMASK | eth0 Interface IP subnet mask | 255.255.255.0 |
| GATEWAY | default IP Gateway | 10.0.11.1 |
Note that on your environment, and depending on the underlying hosting architecture, the interface might get a different name (e.g. ens192, ...)
Example:
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
TYPE="Ethernet"
PROXY_METHOD="none"
BROWSER_ONLY="no"
BOOTPROTO="none"
DEFROUTE="yes"
IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL="no"
IPV6INIT="no"
IPV6_AUTOCONF="yes"
IPV6_DEFROUTE="yes"
IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL="no"
IPV6_ADDR_GEN_MODE="stable-privacy"
NAME="eth0"
UUID="2910018a-36ec-4846-9f87-5d0278ec68ab"
DEVICE="eth0"
ONBOOT="yes"
IPADDR="10.0.11.30"
PREFIX="24"
GATEWAY="10.0.11.1"
DNS1="8.8.8.8"Install a few additional packages
[root@localhost ~]# dnf update -y
[root@localhost ~]# dnf install -y tmux vim tcpdump wireshark libxslt libxml2 wget net-tools mlocate rsync lsof bind-utils chrony graphvizDisable firewalld and selinux. Type commands:
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl stop firewalld
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl disable firewalldUpdate the file selinux in /etc/sysconfig/ in order to prevent SELinux policy from being loaded. Set the parameter SELINUX to "disabled".
[root@localhost ~]# vi /etc/sysconfig/selinuxExample:
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/sysconfig/selinux
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.
SELINUX=disabled
...Check NTP to ensure time synchronization, add ntp server configuration if needed.
[root@localhost ~]# chronyc sources
MS Name/IP address Stratum Poll Reach LastRx Last sample
===============================================================================
^+ ntp1.unix-solutions.be 2 10 377 904 -1318us[-1307us] +/- 37ms
^- webserver.discosmash.com 3 10 373 713 +2133us[+2144us] +/- 74ms
^+ time.cloudflare.com 3 10 377 615 +36us[ +47us] +/- 14ms
^* time.cloudflare.com 3 10 377 487 +521us[ +532us] +/- 14msReboot the server
[root@localhost ~]# rebootSRE components Installation
Common components
The next chapters concern the installation and configuration steps for SRE which are commons to all SRE components (EM's and CP's)
PostgreSQL
Install the repository RPM:
[root@localhost ~]# dnf install -y https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/reporpms/EL-8-x86_64/pgdg-redhat-repo-latest.noarch.rpm
[root@localhost ~]# dnf -qy module disable postgresqlInstall PostgreSQL 14 and the replication manager repmgr_14:
[root@localhost ~]# dnf install -y postgresql14-server repmgr_14Activate the service postgresql-14 such that it starts in the usual runlevels:
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable postgresql-14Enable repmgrd for automatic db switchover
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable repmgr-14Mongodb
INFO
Mongodb is needed only if CAC, the registrar functionality or global cache is used.
On all servers dedicated to Mongo DB (preferably 3 including the Arbiter), execute the following procedure. Create a /etc/yum.repos.d/mongodb-org-5.0.repo file so that you can install MongoDB directly, using dnf:
[root@localhost ~]# cat <<EOF | tee /etc/yum.repos.d/mongodb.repo
[mongodb-org-5.0]
name=MongoDB Repository
baseurl=https://repo.mongodb.org/yum/redhat/8/mongodb-org/5.0/x86_64/
gpgcheck=0
enabled=1
EOFTo install and enable the latest stable version of MongoDB, issue the following command:
[root@localhost ~]# dnf install -y mongodb-org-server mongodb-org-shell
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl start mongod
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable mongodAnsible (optional)
If you plan to use the embedded ansible playbook to upgrade the system, ansible needs to be installed on the system. To do that:
[root@localhost ~]# dnf install -y ansible-coreEpel repository
Epel repository is needed to satisfy SRE dependencies, to add it run:
sudo subscription-manager repos --enable codeready-builder-for-rhel-8-x86_64-rpms
sudo dnf install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-8.noarch.rpm -yInfluxDB and Telegraf repository
Run the following commands to add InfluxDB and Telegraf repository and install telegraf.
[root@localhost ~]# cat <<EOF | tee /etc/yum.repos.d/influxdb.repo
[influxdb]
name = InfluxDB Repository - RHEL \$releasever
baseurl = https://repos.influxdata.com/rhel/\$releasever/\$basearch/stable
enabled = 1
gpgcheck = 1
gpgkey = https://repos.influxdata.com/influxdata-archive_compat.key
EOF
[root@localhost ~]# dnf install -y telegraf
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl disable telegrafEM component
Influx DB
Run the following commands to install InfluxDB.
[root@localhost ~]# dnf install -y influxdb2 influxdb2-cli
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl start influxd
[root@localhost ~]# influx setup -u influxuser -p influxuser -t my-super-secret-token -o influxorg -b bucket -r 1h (it may ask for confirmation)
[root@localhost ~]# influx bucket delete -n bucket
[root@localhost ~]# influx bucket create -n telegraf -o influxorg -r 30dLog aggregation (optional)
Log aggregation is implemented with Graylog. Graylog requires opensearch server. To install it:
[root@localhost ~]# rpm --import https://artifacts.opensearch.org/publickeys/opensearch.pgp
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -Uvh https://artifacts.opensearch.org/releases/bundle/opensearch/2.5.0/opensearch-2.5.0-linux-x64.rpm
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl daemon-reload
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable opensearch.service
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir -p /usr/share/opensearch/config/
[root@localhost ~]# cat > /usr/share/opensearch/config/opensearch.yml << EOF
cluster.name: graylog
path.data: /var/lib/opensearch
path.logs: /var/log/opensearch
action.auto_create_index: false
plugins.security.disabled: true
network.host: 0.0.0.0
discovery.type: single-node
EOF
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl start opensearchTo install graylog server run:
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -Uvh https://packages.graylog2.org/repo/packages/graylog-5.0-repository_latest.rpm
[root@localhost ~]# dnf install -y graylog-serverCP component
Kamailio
You can install the Kamailio packages from the official repository, as shown in the following commands.
[root@localhost ~]# dnf -y install dnf-plugins-core
[root@localhost ~]# dnf config-manager --add-repo https://rpm.kamailio.org/centos/kamailio.repo
[root@localhost ~]# dnf install --disablerepo=kamailio --enablerepo=kamailio-5.7.0 kamailio kamailio-pythonIf you plan to use SRE as a SIP registrar you need also the kamailio-mongodb package.
Install it with:
[root@localhost ~]# dnf install --disablerepo=kamailio --enablerepo=kamailio-5.7.0 kamailio-mongodb