Introduction
The Alarm Guide describes the available alarms in version 3.3 of SRE, along with their description, monitored operations, SNMP configuration and MIBS description.
Alarming Dashboard
Alarms are presented to SRE administrators in two places: notifications in the main SRE banner and the Alarms page accessible through System > Alarms.
The SRE raises alarms when thresholds are reached for the operations listed in this document. As soon as the situation is back to normal, the system automatically clears the corresponding alarm (see Clearance below). Manual clearance is possible, but it does not fix the situation that has caused the alarm: if a node or a SIP Agent is down or if a process is stopped, manually clearing the alarm will not restore connections or restart processes.
Alarm notification
Alarm notifications appear in the four squares on the right in the main SRE banner, one square for each severity from info to critical.
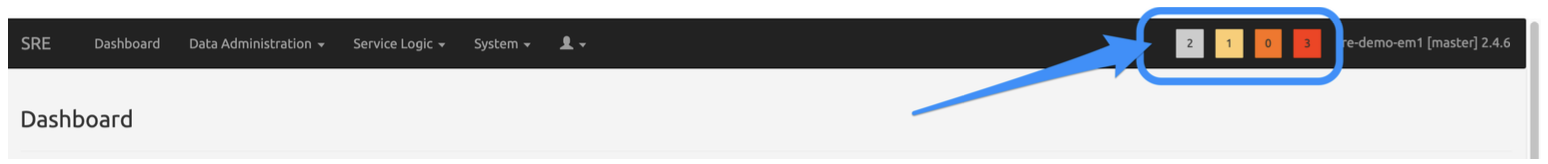
Only active alarms are counted in the number displayed. Clicking on any square opens the Alarms page with the appropriate filters: alarm status is « Active », alarm severity is any of the four severities depending on the square clicked.
The picture below shows the Alarms page when the « critical » square (3) has been clicked. The 3 active critical alarms are listed on this page.
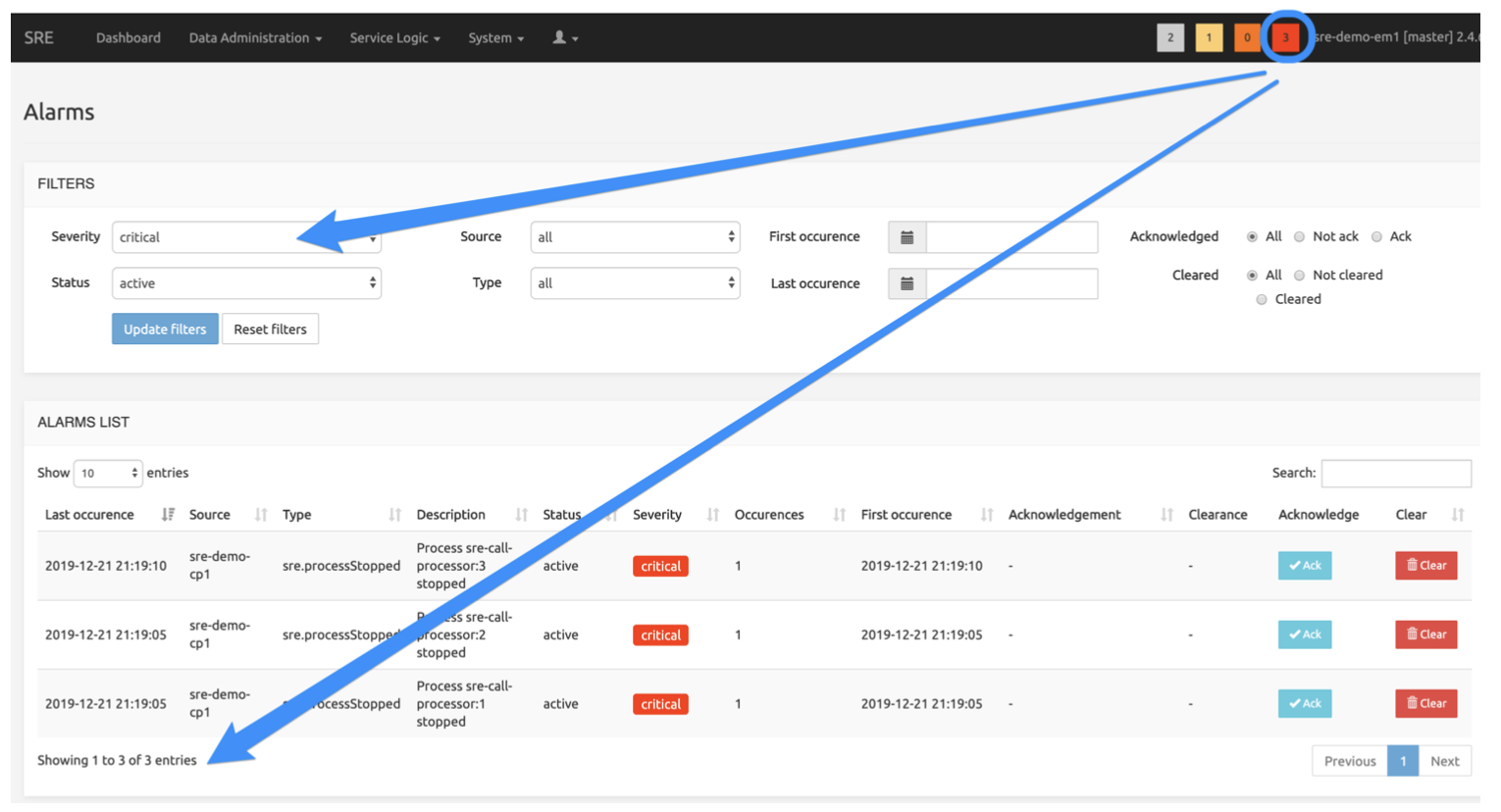
Alarms page
From the System menu entry in the main menu bar, selecting Alarms displays the Alarms page with default filters, retrieving all alarms recorded in the DB.
The FILTERS section allows specifying the following criteria:
Severity: all levels or any level from info to critical
Status: all statuses or a status active, user-cleared, system-cleared
Source: all nodes or any of the EM nodes and CP nodes present in the system
Type: all alarm types or any of the types. Only the types actually present in DB for the Severity filter already selected are listed, i.e. alarm types for which no alarm has been raised do not show in the list -- querying the DB on non-existing alarms is useless.
First and last occurrence: starting and ending dates for the desired time window to query.
Acknowledged: all alarms (acknowledgement ignored), or only the acknowledged ones, or only the not acknowledged ones
Cleared: all alarms (clearance ignored), or only the cleared ones, or only the not cleared ones.
When all filters have been set as desired, click the Update filters button to refresh the list of alarms. Note that clicking Reset filters clears up all filters and queries the DB using default filters (all alarms, of all severities, statuses, sources and types).
The ALARM LIST section returns the alarms matching the criteria selected above. The usual Search field and navigation controls are available.
The Description field provides details about the situation that has raised an alarm.
The Occurrences field marks recurrent alarms. An alarm is considered recurrent (and the number of occurrences is incremented) when a threshold is again reached for an alarm already existing in DB, for the same source with the same type and severity, in the active state (not system- or user-cleared) and the new alarm occurs after the delay set in Settings / Alarms / Alarms recurrence window (default: 60 secs).
Should the new alarm occur within the 60 secs recurrence time window, it would just be ignored (to avoid a useless increase of alarm-related data). After the 60 secs delay, a new alarm (for the same source with the same type and severity) would be created only if the state of the existing alarm(s) is not active.
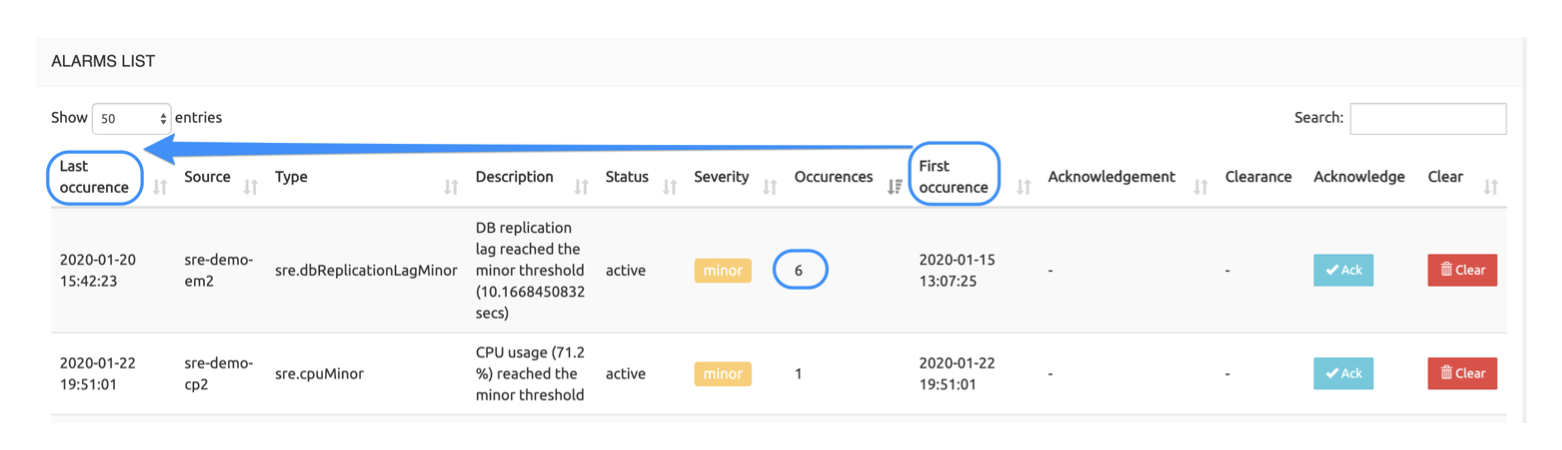
The two columns Last occurrence and First occurrence show the time and date of the last and first occurrences of the alarm. If the number of occurrences is 1, they are identical. If it is > 1, the comparison of the two values gives an indication of the time elapsed between the first and last occurrence (5 days in the example below, during which the alarm occurred 6 times).
Managing Alarms
SRE alarms record situations when a threshold is reached. User management of alarms is limited to two actions through the Ack and Clear buttons on each line of the list:
Acknowledgment: clicking the Ack button changes the status from not ack to ack and stores the action's time, date and user ID. This shows other administrators that one operator has seen this alarm. This action cannot be reverted (no un-ack).
Clearance: the system automatically clears up most alarms as soon as the monitoring measurement shows that the threshold is not reached anymore. The status changes from active to system-cleared and the time and date of the clearance are stored.
Active alarms can also be cleared manually by clicking the Clear button: the status changes from active to user-cleared. The time, date and user ID are stored. This action, be it system- or user-applied, cannot be reverted (no unclear). It is not possible to delete an alarm record from the table.
SNMP Configuration
SNMP allows the network administrators of SRE to monitor the system through SNMP traps, that is, to be alerted in case an issue occurs which results in a trap notification being sent to the target OSS system.
SNMP Configuration is done in the GUI page System > Settings. SRE supports SNMP v1/2 and SNMP v3.
The Alarms tab allows adding SNMP trap receivers and setting the thresholds for various types of events. SNMPv3 trap receivers can be specified on top of standard SNMP ones. "SNMP trap receivers" are used for SNMP v1/v2, while "SNMP v3 traps receivers" are used for SNMP v3.
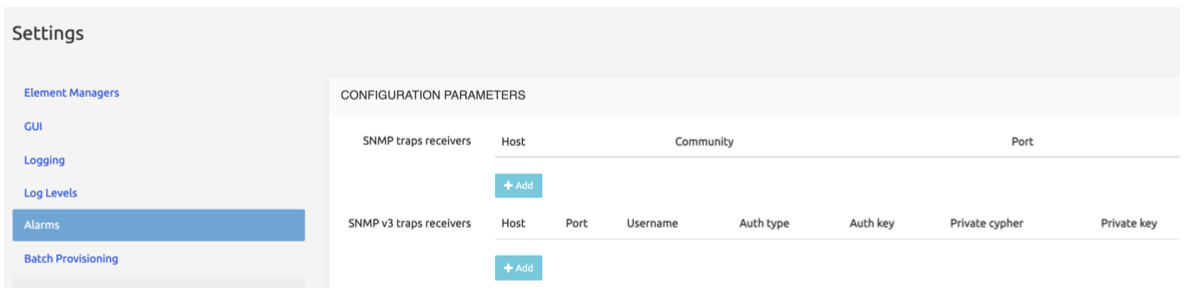
The common fields for the two types of receivers/targets are:
Host
Community (default: public)
Port (default: 162)
On SNMP v3 traps receivers the Admin also needs to specify:
Username
Auth type: MD5, SHA, SHA224, SHA256, SHA384, SHA512
Auth key
Private cipher: AES128, AES192, AES256
Private key
Email Configuration
On top of standard SNMP events, it's possible to receive emails in case an issue occurs in SRE.
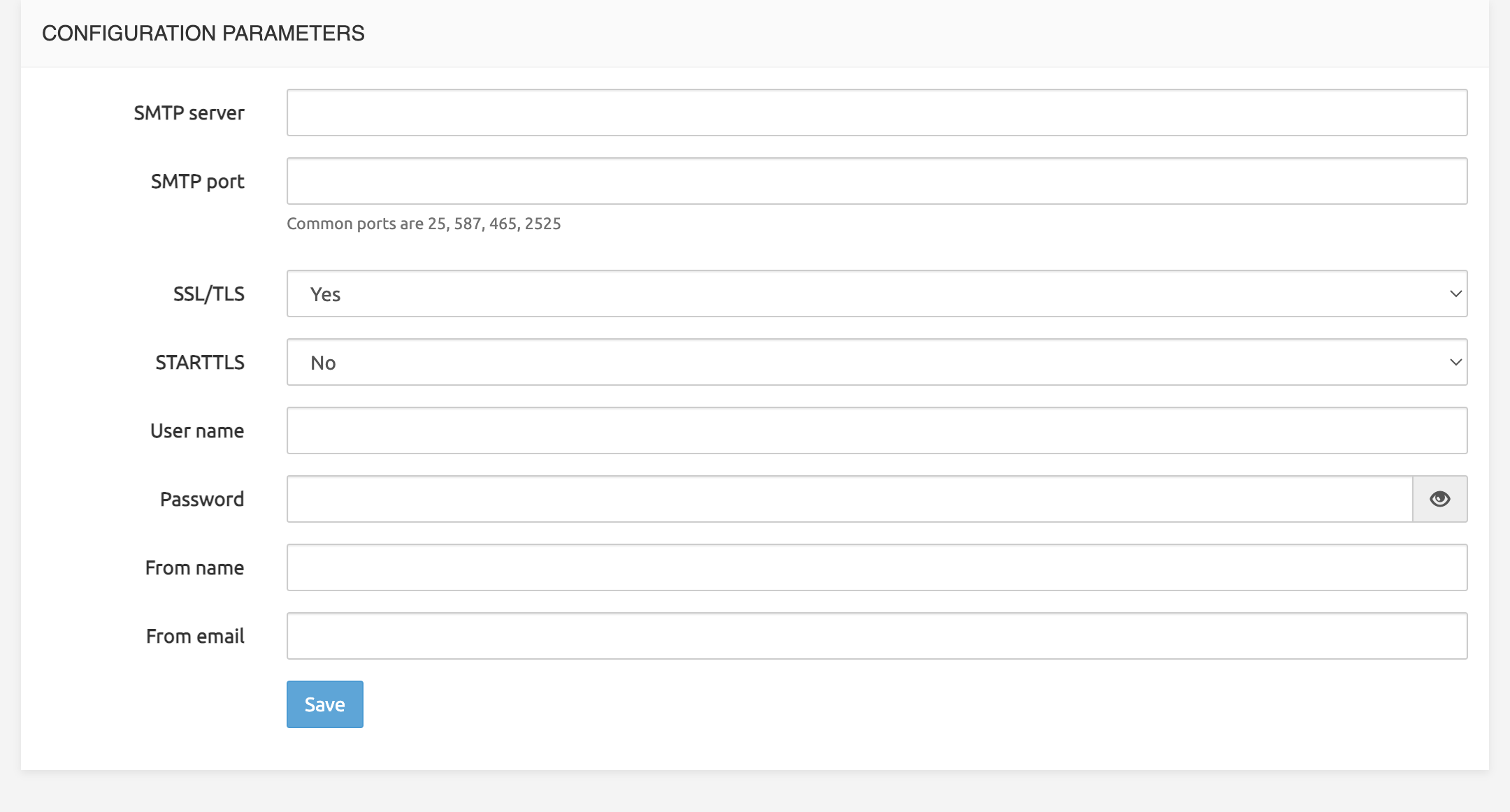
SMTP server configuration
SMTP Configuration is done in the GUI page System > Settings. The SMTP tab supports the following settings:
SMTP Server: address or hostname of relaying smtp server
SMTP Port: port of relaying smtp server
SSL/TLS: enable secure communication
START-TLS: enable encrypted communication after unencrypted handshake
Username: used for authentication with SMTP server
Password: used for authentication with SMTP server
From name
From email
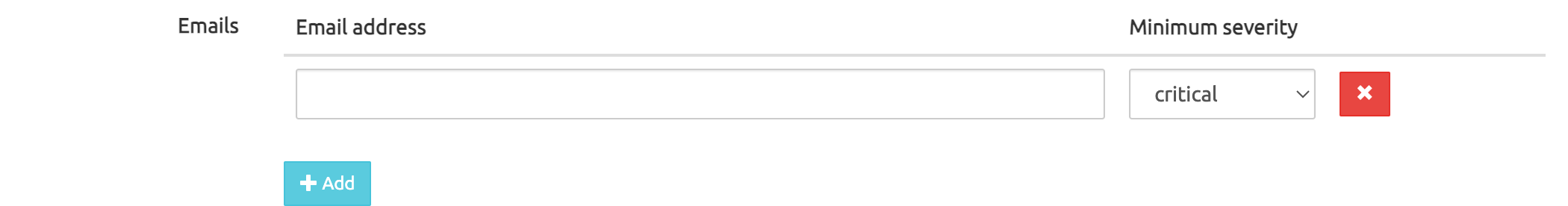
Recipients configuration
Email Configuration is done in the GUI page System > Settings. The Alarms tab allows adding email addresses and setting the threshold based on alarm severity.
Alarm thresholds
For various categories, it is possible to modify the default thresholds in SRE to trigger alarms and SNMP traps. Most thresholds are defined per category and severity (minor, major, critical).
The available categories are those for which the 3 thresholds can be set:
CPU Usage
Memory usage
Disk usage (per partition)
INVITE processing performance
REGISTER processing performance
OPTIONS processing performance
ENUM NAPTR processing performance
DB replication lag
Furthermore, the following settings are available:
Alarms recurrence window (secs): alarms of the same type which fall within the defined time window are grouped together
Check interval for cdrs (mins): the time window within which it is expected that at least a cdr file is created. The default value of 0 means that this check is skipped
Kamailio shared memory usage alarm threshold
Number of days to alert before the certificate expires
Interval for checking record count increase/decrease (secs): the record count of tables will be checked every period defined by this setting
Percentage threshold for record count
Alarms description
The SRE permanently (every 4 seconds) monitors the conditions for the operations presented in the table below, and raises alarms when corresponding thresholds are reached.
Four severity levels are used:
Info: a simple information message, not linked to any threshold
Minor: raised when the minor threshold is reached. When Minor is detected, it clears Major and Critical alarms of the same type
Major: raised when the major threshold is reached. When Major is detected, it clears a Critical alarm of the same type
Critical: raised when the critical threshold is reached
The following alarms are exceptions namely by the fact that they do not get automatically cleared but require a manual action from the SRE Admin or User:
- mongoDBMemberStateChanged
- licensingPlatformLimitReached
- licensingCallProcessorLimitReached
- licensingEnumProcessorLimitReached
- licensingHttpProcessorLimitReached
- expiredCert
- recordCount
- kamailioLowMemory
- missingCDR
- Service Logic Error
- Service Logic Jump
MIBS - Traps
All traps OID have the following OID prefix: 1.3.6.1.4.1.38433.5.3.0
System
| Monitored operation | Severity | SNMP messages | Objects | Description | Trap OID suffix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPU usage | minor | 'cpuMinor' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when CPU usage reached the minor threshold (%) | .1.11 |
| CPU usage | major | 'cpuMajor' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when CPU usage reached the major threshold (%) | .1.12 |
| CPU usage | critical | 'cpuCritical' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when CPU usage reached the critical threshold (%) | .1.13 |
| CPU usage | info | 'cpuNormal' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when CPU usage is back to normal (< minor) | .1.13 |
| Memory usage | minor | 'memoryMinor' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when memory reached the minor threshold (%) | .1.7 |
| Memory usage | major | 'memoryMajor' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when memory reached the major threshold (%) | .1.8 |
| Memory usage | critical | 'memoryCritical' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when memory reached the critical threshold (%) | .1.9 |
| Memory usage | info | 'memoryNormal' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when memory is back to normal (< minor) | .1.10 |
| Disks usage | minor | 'diskMinor' | {node, description, severity, mountPoint} | Generated when disk usage (on the specific mount point/partition) reached the minor threshold | .1.15 |
| Disks usage | major | 'diskMajor' | {node, description, severity, mountPoint} | Generated when disk usage (on the specific mount point/partition) reached the major threshold | .1.16 |
| Disks usage | critical | 'diskCritical' | {node, description, severity, mountPoint} | Generated when disk usage (on the specific mount point/partition) reached the critical threshold | .1.17 |
| Disks usage | info | 'diskNormal' | {node, description, severity, mountPoint} | Generated when disk usage (on the specific mount point/partition) is back to normal (< minor) | .1.18 |
Service Logic: SIP messages processing duration (performance)
| Monitored operation | Severity | SNMP messages | Objects | Description | Trap OID suffix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INVITE Performance | minor | 'invitePerformanceMinor' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when INVITE performance reached the minor threshold (msec) | .1.19 |
| INVITE Performance | major | 'invitePerformanceMajor' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when INVITE performance reached the major threshold (msec) | .1.20 |
| INVITE Performance | critical | 'invitePerformanceCritical' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when INVITE performance reached the critical threshold (msec) | .1.21 |
| INVITE Performance | info | 'invitePerformanceNormal' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when INVITE performance is back to normal | .1.22 |
| REGISTER Performance | minor | 'registerPerformanceMinor' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when REGISTER performance reached the minor threshold (msec) | .1.23 |
| REGISTER Performance | major | 'registerPerformanceMajor' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when REGISTER performance reached the major threshold (msec) | .1.24 |
| REGISTER Performance | critical | 'registerPerformanceCritical' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when REGISTER performance reached the critical threshold (msec) | .1.25 |
| REGISTER Performance | info | 'registerPerformanceNormal' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when REGISTER performance is back to normal | .1.26 |
| OPTIONS Performance | minor | 'optionsPerformanceMinor' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when OPTIONS performance reached the minor threshold (msec) | .1.27 |
| OPTIONS Performance | major | 'optionsPerformanceMajor' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when OPTIONS performance reached the major threshold (msec) | .1.28 |
| OPTIONS Performance | critical | 'optionsPerformanceCritical' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when OPTIONS performance reached the critical threshold (msec) | .1.29 |
| OPTIONS Performance | info | 'optionsPerformanceNormal' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when OPTIONS performance is back to normal | .1.30 |
| ENUM NAPTR Performance | minor | 'naptrPerformanceMinor' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when NAPTR performance reached the minor threshold (msec) | .1.71 |
| ENUM NAPTR Performance | major | 'naptrPerformanceMajor' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when NAPTR performance reached the major threshold (msec) | .1.72 |
| ENUM NAPTR Performance | critical | 'naptrPerformanceCritical' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when NAPTR performance reached the critical threshold (msec) | .1.73 |
| ENUM NAPTR Performance | info | 'naptrPerformanceNormal' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when NAPTR performance is back to normal | .1.74 |
Service Logic: Error during node execution (no SNMP trap)
| Monitored operation | Severity | SNMP messages | Objects | Description | Trap OID suffix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Service Logic Error | info | N/A (no trap) | N/A | Error in executing the service logic | N/A |
| Service Logic Jump | info | N/A (no trap) | N/A | Jump to next node failed | N/A |
Node status
| Monitored operation | Severity | SNMP messages | Objects | Description | Trap OID suffix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| node is unavailable | critical | 'nodeUnavailable' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when node is unavailable | .1.65 |
| node is available | info | 'nodeAvailable' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when node is available | .1.66 |
Supervisord: process responsible for automatic launch and relaunch of processes
| Monitored operation | Severity | SNMP messages | Objects | Description | Trap OID suffix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| process is stopped | critical | 'processStopped' | {node, description, severity, processName} | Generated when a process has stopped | .1.1 |
| process restarted less than 5 seconds ago | info | 'processStarting' | {node, description, severity, processName, processPID} | Generated when a process is starting | .1.2 |
| process start | info | 'processStarted' | {node, description, severity, processName, processPID} | Generated when a process is started | .1.3 |
Pacemaker: daemon for clustering of call processors
| Monitored operation | Severity | SNMP messages | Objects | Description | Trap OID suffix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pacemaker node is down | critical | 'pacemakerNodeDown' | {node, description, severity, pacemakerHost} | Generated when pacemaker node is down | .1.54 |
| pacemaker node is up | info | 'pacemakerNodeUp' | {node, description, severity, pacemakerHost} | Generated when pacemaker node is up | .1.55 |
| pacemaker node is locked | info | 'pacemakerNodeLocked' | {node, description, severity, pacemakerHost} | Generated when pacemaker node is locked | .1.56 |
| pacemaker quorum is lost | critical | 'pacemakerQuorumLost' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when pacemaker quorum is lost | .1.57 |
| pacemaker quorum reached | info | 'pacemakerQuorumReached' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when pacemaker quorum is reached | .1.58 |
| pacemaker resource is down | critical | 'pacemakerResourceDown' | {node, description, severity, pacemakerResource} | Generated when pacemaker resource is down | .1.59 |
| pacemaker resource is up | info | 'pacemakerResourceUp' | {node, description, severity, pacemakerResource} | Generated when pacemaker resource is up | .1.60 |
| pacemaker resource is locked | info | 'pacemakerResourceLocked' | {node, description, severity, pacemakerResource} | Generated when pacemaker resource is locked | .1.61 |
CDR Collector availability
| Monitored operation | Severity | SNMP messages | Objects | Description | Trap OID suffix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cdr collector is unreachable | major | 'cdrCollectorDown' | {node, description, severity, collectorHost} | Generated when CDR is down | .1.50 |
| cdr collector is reachable | major | 'cdrCollectorUp' | {node, description, severity, collectorHost} | Generated when CDR is up | .1.51 |
SIP Agents
| Monitored operation | Severity | SNMP messages | Objects | Description | Trap OID suffix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| agentDown | info | 'sipAgentDown' | {node, description, severity, agentName, agentAddress, agentPort, agentTransport} | Generated when a SIP agent is unreachable | .1.4 |
| agentTrying | info | 'sipAgentTrying' | {node, description, severity, agentName, agentAddress, agentPort, agentTransport} | Generated when a SIP agent status is still unknown | .1.5 |
| agentUp | info | 'sipAgentUp' | {node, description, severity, agentName, agentAddress, agentPort, agentTransport} | Generated when a SIP agent is reachable | .1.6 |
Postgres DB Replication
| Monitored operation | Severity | SNMP messages | Objects | Description | Trap OID suffix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| disconnected | critical | 'replicationNodeDBDisconnected' | {node, description, severity, standbyNode} | Generated when a node DB disconnected from replication | .1.31 |
| connected | info | 'replicationNodeDBConnected' | {node, description, severity, standbyNode} | Generated when a node DB connected for replication | .1.32 |
| Lag (between write on master and write on slave) | minor | 'replicationLagMinor' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when replication lag reached the minor threshold (sec.) | .1.33 |
| Lag (between write on master and write on slave) | major | 'replicationLagMajor' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when replication lag reached the major threshold (sec.) | .1.34 |
| Lag (between write on master and write on slave) | critical | 'replicationLagCritical' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when replication lag reached the critical threshold (sec.) | .1.35 |
| Lag (between write on master and write on slave) | critical | 'replicationLagNormal' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when replication lag is back to normal (< minor) | .1.36 |
MongoDB
| Monitored operation | Severity | SNMP messages | Objects | Description | Trap OID suffix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MongoDB down | critical | 'localMongoDBDown' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when connection to MongoDB on localhost fails | .1.38 |
| MongoDB up | info | 'localMongoDBUp' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when connection to MongoDB on localhost is successful | .1.37 |
| No primary | critical | 'mongoDBNoPrimary' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when no primary is active in the MongoDB replicaset | .1.39 |
| Primary is present | info | 'mongoDBPrimary' | {node, description, severity, mongoDBMember} | Generated when a primary is active in the MongoDB replicaset | .1.40 |
| Node state change | major | 'mongoDBMemberStateChanged' | {node, description, severity, mongoDBMember} | Generated when the state of a MongoDB replicaset member changes | .1.41 |
InfluxDb
| Monitored operation | Severity | SNMP messages | Objects | Description | Trap OID suffix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| InfluxDb instance is down | minor | 'influxDBUnavailable' | {node, description, severity, influxdbHostname} | Generated when influxdb is unavailable | .1.62 |
| InfluxDb instance is up | info | 'influxDBAvailable' | {node, description, severity, influxdbHostname} | Generated when influxdb is available | .1.63 |
Licensing
| Monitored operation | Severity | SNMP messages | Objects | Description | Trap OID suffix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| System-wide SIP License Limit Reached | major | 'licensingPlatformLimitReached' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when the limit of system-wide CAPS (SIP interface) is reached as an average in at least a burst window (10 sec.) | .1.42 |
| SIP Call Processor Limit | major | 'licensingCallProcessorLimitReached' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when calls count reached the call processor hard limit during the last burst window | .1.43 |
| HTTP Processor Limit | major | 'licensingHttpProcessorLimitReached' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when request count reached the HTTP processor hard limit during the last burst window | .1.45 |
| ENUM Processor Limit | major | 'licensingEnumProcessorLimitReached' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when ENUM request count reached the ENUM processor hard limit during the last burst window | .1.46 |
Custom Alarms
| Monitored operation | Severity | SNMP messages | Objects | Description | Trap OID suffix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| customAlarm | configurable by node | 'customAlarm' | {node, description, severity, customAlarmType, customAlarmDescription} | Custom alarm generated by service logic node | .1.44 |
| customAlarmClear | info | 'customAlarmClear' | {node, description, severity, customAlarmType} | Custom alarm cleared by service logic node. For an alarm to be cleared, the customAlarmType of the clearing must match that of the customAlarm | .1.47 |
CDR
| Monitored operation | Severity | SNMP messages | Objects | Description | Trap OID suffix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Missing CDR | critical | 'missingCDR' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when no CDR is produced during an interval specified in System Settings | .1.48 |
Kamailio
| Monitored operation | Severity | SNMP messages | Objects | Description | Trap OID suffix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kamailio Low Memory | major | 'kamailioLowMemory' | {node, description, severity} | Generated when kamailio memory usage reaches the threshold | .1.49 |
Certificate
| Monitored operation | Severity | SNMP messages | Objects | Description | Trap OID suffix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Certificate expiration | major | 'expiredCert' | {node, description, severity, certificate} | Generated when a certificate is about to expire | .1.52 |
DB changes
| Monitored operation | Severity | SNMP messages | Objects | Description | Trap OID suffix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB record count | major | 'recordCount' | {node, description, severity, datamodel, table, oldCount, newCount} | Generated when record count increases or decreases above threshold | .1.53 |
MIBS - Objects
| Object Name | Syntax | OID .1.3.6.1.4.1.38433.5 + |
|---|---|---|
| node | DisplayString | .2.1 |
| description | DisplayString | .2.2 |
| severity | INTEGER { info ( 0 ) ,warning ( 10 ) , minor( 20 ) , major ( 30 ) ,critical ( 40 ) } | .2.3 |
| processName | DisplayString | .2.4 |
| processPID | Integer32 | .2.5 |
| agentName | DisplayString | .2.6 |
| agentAddress | IpAddress | .2.7 |
| agentPort | Integer32 | .2.8 |
| agentTransport | INTEGER { udp ( 0 ) ,tcp ( 1 ) } | .2.9 |
| standbyNode | DisplayString | .2.10 |
| mountPoint | DisplayString | .2.11 |
| mongoDBMember | DisplayString | .2.12 |
| customAlarmType | DisplayString | .2.13 |
| customAlarmDescription | DisplayString | .2.14 |
| startInterval | DisplayString | .2.15 |
| endInterval | DisplayString | .2.16 |
| collectorHost | DisplayString | .2.17 |
| certificate | DisplayString | .2.18 |
| datamodel | DisplayString | .2.19 |
| table | DisplayString | .2.20 |
| oldCount | DisplayString | .2.21 |
| newCount | DisplayString | .2.22 |
| pacemakerHost | DisplayString | .2.23 |
| pacemakerResource | DisplayString | .2.24 |
| influxdbHostname | DisplayString | .2.25 |
High-level actions upon alarm generation
The following table lists possible actions to execute, upon receiving one or more application alarms described in this document. It is understood that the described operations will require technical knowledge of the SRE system, as well as further documentation such as the Operations&Monitor document.
+-----------------+-----------------+------------------------------+-----------------+ | Alarm | Description | Troubleshooting action | OaM guide | +=================+=================+==============================+=================+ | CPU Usage | The CPU on a | Verify with the | Section 3.3 for | | | virtual machine | command "top" | monitoring the | | | is on high | what is the | CPU usage. | | | consumption | process, or | | | | | list of | Section 1/2 for | | | | processes, that | restarting the | | | | are most | SRE | | | | consuming the | pro | | | | CPU resources. | cesses/services | | | | If in abnormal | | | | | consumption, | | | | | you can restart | | | | | the process and | | | | | check it does | | | | | not end up in | | | | | the same | | | | | situation. | | +-----------------+-----------------+------------------------------+-----------------+ | Memory Usage | The available | Verify with the | Section 3.3 for | | | memory on a | commands "top" | monitoring the | | | virtual machine | and "free" what | memory usage. | | | is on high | is the memory | | | | consumption | situation and | Section 1/2 for | | | | the process, or | restarting the | | | | list of | SRE processes | | | | processes, that | | | | | are most | | | | | consuming | | | | | memory. If in | | | | | abnormal | | | | | consumption, | | | | | you can restart | | | | | the process and | | | | | check it does | | | | | not end up in | | | | | the same | | | | | situation. | | +-----------------+-----------------+------------------------------+-----------------+ | Disks Usage | A partition in | In most cases, | Section 3.1 and | | | the file system | /var/log gets | 3.2 | | | is occupied | filled up due | | | | over the | to high traffic | | | | thresholds | and log-levels | | | | | producing too | | | | | many log lines | | | | | for the | | | | | automatic log | | | | | rotation. In | | | | | such a case, | | | | | you can safely | | | | | remove the logs | | | | | which occupy | | | | | the most, | | | | | making sure you | | | | | don't delete | | | | | the currently | | | | | open log file | | | | | (e.g. sre.log) | | | | | but only those | | | | | of past days | | | | | (e.g. | | | | | sre.log.2023-05-02). | | | | | For different | | | | | partitions, | | | | | you'll need to | | | | | verify with | | | | | standard linux | | | | | commands which | | | | | directory | | | | | within the | | | | | partition is | | | | | taking more | | | | | disk space and | | | | | take action | | | | | accordingly. | | | | | Particular | | | | | attention must | | | | | be given to | | | | | database | | | | | directories | | | | | (/var/lib/pgsql | | | | | and | | | | | /data | | | | | /sre/location), | | | | | since they | | | | | cannot get | | | | | freed without | | | | | risks by a | | | | | manual deletion | | | | | of files. | | +-----------------+-----------------+------------------------------+-----------------+ | INVITE | The performance | An analysis of | Section 3.2 for | | Performance | of processing | the service | monitoring the | | | INVITE as an | logic execution | CPU usage. | | | average over | must be carried | | | | the observation | out from debug | Section 1/2 for | | | period (5 | logs | restarting the | | | minutes) is | (t | SRE processes | | | beyond the | racing.summary) | | | | acceptable | in order to | | | | thresholds | understand if | | | | | this behavior | | | | | is caused by a | | | | | subset of | | | | | calls, if it | | | | | only happens on | | | | | a specific CP | | | | | node, or if | | | | | it's instead | | | | | generalized | | | | | over all calls. | | | | | | | | | | Statistics in | | | | | "stats counter" | | | | | tab can also be | | | | | checked. | | | | | Especially the | | | | | section | | | | | displaying the | | | | | stats | | | | | performance per | | | | | SL node in | | | | | order to | | | | | pinpoint if a | | | | | specific node | | | | | takes a long | | | | | time. | | | | | | | | | | CPU usage can | | | | | be also | | | | | checked. | | +-----------------+-----------------+------------------------------+-----------------+ | Process Stopped | A process which | In the first | Section 3.4.1 | | | was previously | place it must | to know the | | | started has | be checked | relevant | | | stopped | whether the | processes for | | | | process is | the type of | | | | relevant for | node. | | | | the type of | | | | | node (EM vs CP) | Section 4.2 for | | | | and for the | checking the | | | | specific SRE | logs. | | | | deployment.\ | | | | | If the process | Section 1 for | | | | should be | process restart | | | | effectively | | | | | running, you | | | | | need to check | | | | | the SRE logs | | | | | related to the | | | | | process to | | | | | understand the | | | | | root cause, and | | | | | restart the | | | | | process through | | | | | supervisorctl | | | | | commands | | +-----------------+-----------------+------------------------------+-----------------+ | Agent down | A SIP Agent | An analysis on | Section 11 | | | (sip peer of | the target sip | related to | | | SRE) is | peer must be | sngrep tool | | | replying with a | carried out. | | | | rejection to | | | | | SIP OPTIONS | Use sngrep tool | | | | sent by an SRE | on the SRE to | | | | CP | confirm that no | | | | | answer is | | | | | received for | | | | | the SIP | | | | | OPTIONS. | | +-----------------+-----------------+------------------------------+-----------------+ | Agent trying | An SRE CP is | Verify with the | Section 10 | | | not receiving | help of sngrep, | related to | | | anymore a | tcpdump or a | sngrep tool | | | response to SIP | monitoring tool | | | | OPTIONS sent to | that | | | | a specific SIP | effectively no | | | | Agent | answers are | | | | | received at the | | | | | CP level upon | | | | | SIP OPTIONS. | | | | | The possible | | | | | cause might | | | | | reside in the | | | | | underlying | | | | | network | | | | | (routing, | | | | | firewalls, ...) | | +-----------------+-----------------+------------------------------+-----------------+ | Postgres DB | A node (EM | Verify the | Section 3.1 for | | Disconnected | master or EM | service | file system | | | standby / CP) | "postgresql-14" | monitoring | | | has the local | (running / | | | | instance of | inactive), the | Section 3.5 for | | | Postgres DB | Postgres logs, | postgres | | | unavailable | and the disk | monitoring. | | | | space on the | | | | | partitions / | | | | | and /data. If | | | | | the problem is | | | | | disk space the | | | | | service will | | | | | not be able to | | | | | restart, so it | | | | | must be freed | | | | | upfront. | | +-----------------+-----------------+------------------------------+-----------------+ | Postgres DB | The replication | If it only | | | Replication Lag | of the database | happens a few | | | | on a standby | times and it | | | | node has taken | doesn't occur | | | | longer than the | again, it's a | | | | thresholds | temporary | | | | | condition due | | | | | to the | | | | | underlying | | | | | network, | | | | | therefore no | | | | | action is | | | | | required. If | | | | | instead it's a | | | | | permanent issue | | | | | that keeps | | | | | occurring, it | | | | | must be | | | | | investigated in | | | | | terms of round | | | | | trip delay | | | | | between the | | | | | standby node | | | | | and the master | | | | | node (ping from | | | | | the standby to | | | | | the master), as | | | | | well as the | | | | | availability of | | | | | all Postgres | | | | | WALS files | | | | | ( | | | | | /data/sre/wals) | | | | | on the standby | | | | | node as in the | | | | | master | | +-----------------+-----------------+------------------------------+-----------------+ | MongoDB down | A specific node | Check the mongo | Mongo status: | | | (e.g. CP) has | logs | section 3.7.1 | | | its local | ( | | | | instance of | /var/log/mongo) | Mongo restart: | | | MongoDB | to understand | . section 2.4 | | | stopped, | the condition | | | | whereas it | that led to a | | | | should be | stop. It is | | | | running. This | possible that | | | | doesn't affect | disk space is | | | | Call Admission | causing the | | | | Control as long | issue. Try to | | | | as a PRIMARY is | restart the | | | | available. | service mongod | | | | | and check the | | | | | startup process | | | | | through | | | | | systemctl and | | | | | journalctl if | | | | | it doesn't | | | | | start again. | | | | | Also, verify on | | | | | other nodes | | | | | that mongo is | | | | | running and | | | | | that a PRIMARY | | | | | node is | | | | | available. | | +-----------------+-----------------+------------------------------+-----------------+ | MongoDB No | There is no | Verify MongoDB | Mongo Replica | | Primary Node | elected PRIMARY | status on the | set status: | | | node of | unavailable | section 3.7.2 | | | MongoDB. This | nodes. Try to | | | | happens when at | restart the | Mongo | | | least half of | service mongod | restart:section | | | the Mongo | or check | 2.4 | | | instances are | systemctl and | | | | stopped. | journalctl in | | | | | case it doesn't | | | | | start again. In | | | | | order to have a | | | | | PRIMARY node | | | | | back, you'll | | | | | need to restore | | | | | at least half + | | | | | 1 mongoDB | | | | | nodes. | | +-----------------+-----------------+------------------------------+-----------------+ | MongoDB Node | A node that | Typically there | Mongo status: | | State Changed | used to be | is no urgent | section 3.7.1 | | | PRIMARY has | action related | | | | changed its | to this. Check | | | | state to | mongoDB logs | | | | SECONDARY | and verify that | | | | | the cluster has | | | | | elected a new | | | | | PRIMARY. | | +-----------------+-----------------+------------------------------+-----------------+ | Missing CDR | The accounting | Verify that the | Process status: | | | master did not | process | section 1 | | | produce CDR | sr | | | | files in the | e-cdr-collector | Logs: section | | | time frame | is running. If | 3.2 | | | configured in | so, check that | | | | the Settings | sre-cdr-sender | | | | | is running on | | | | | CP nodes. | | | | | Verify the | | | | | sre-cdr-sender | | | | | logs on master | | | | | EM, then verify | | | | | that CP nodes | | | | | are producing | | | | | events | | +-----------------+-----------------+------------------------------+-----------------+ | CDR collector | cdr-sender | Verify that the | Process status: | | is down | process on CP | process | section 1 | | | could not | sr | | | | connect to | e-cdr-collector | Logs: section | | | cdr-collector | is running. If | 3.2 | | | process running | so, check that | | | | on EM. | sre-cdr-sender | | | | | is running on | | | | | CP nodes. | | | | | Verify connectivity between | | | | | CP and EM on port 10002 with | | | | | tcpdump. | | +-----------------+-----------------+------------------------------+-----------------+
